In Modern Radiology Machines What Heats Up the Filament
In the vacuum tube of the x-ray machine the point where the electron. Electrons build at the cathode and through a process called thermionic emission these electrons are then released from the.
Anatomy Of The X Ray Machine Veterian Key
A small increase in the filament voltage 1 results in a large increase in tube current 2 which accelerates high speed electrons from the very high temperature filament negative cathode.

. Modern multipurpose xray tube are dual focus tubes. Many of the limitations of standard x-ray tubes lie in the. In modern radiology machines what heats up the filament.
If the X-ray tube anode is allowed to surpass the vapor pressure point of the target material ions will be liberated. Electrons in the outermost orbital shells. The focal point of the filament ends up becoming hot while transmitting the.
When the electrons strike the anode part of their energy is converted into x-ray photons and part is converted to heat. The electrons heat the anode. The tungsten cathode needs to be heated for thermionic emission to take place.
By heating a filament which releases electrons by thermionic emission accelerating electrons with a high. In the vacuum tube of the x-ray machine the point where the electron. A disadvantage of digital radiography is.
As explained in Chapter 4 heat speeds up the movement of the electrons in their orbits and increases their distance from the nucleus. In modern Radiology machines what heats up the filament. Electron production occurs when the filament is heated to around 2000 C this is achieved by passing a current through the filament.
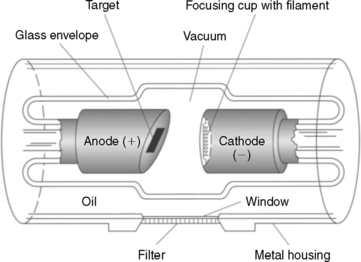
PACS CR DR Digital Systems. The heart of an X-ray machine is an electrode pair-- a cathode and an anode -- that sits inside a glass vacuum tube. It is made of Pyrex glass and encased in a sturdy lead-lined metal.
It glows white hot and the electrons. In modern radiology machines what heats up the filament. Modern x-ray tube 1.
To summarize x-rays are produced in a standard way. It is designed and shaped so that when the x-ray machine is powered up electrons will literally boil off the filament. What is A disadvantage of digital radiography.
PACS CR DR Digital Systems. Thus a 10 voltage potential difference and 3-6 amperes of filament current is supplied which. When energy is applied the filament heats up.
It situated in the focusing cup that directs its. In the vacuum tube of the x-ray machine the point where the. The x-ray tube is the component of the radiographic system that produces the x-rays.
The primary purpose of the filament circuit is to supply a low current to heat the x-ray tube filament for thermionic emission of electrons. The cathode is a heated filament like you might find in an older fluorescent. A disadvantage of digital radiography is.
The working mechanism of the X-ray machine entails the generation of heat. Their cathode assemblies contain two filaments one large and one small. The filament circuit is activated any.
These ions are attracted back toward the helical tungsten filament and begin. The temperature of the filament.

Production Of X Rays Frcr Physics Notes

X Ray Generator And X Ray Tube Components Are Illustrated The X Ray Download Scientific Diagram

Chapter 3 Components Of An X Ray Machine Objectives How X Rays Are Produced By An X Ray Tube X Ray Tube Construction Anode Heel Effect X Ray Tube Warm Up Generator Rectifier Transformer Line Voltage Compensator And Operator S Console

Comments
Post a Comment